Core Principles of Quantum Computing:
- Qubits Functionality: Qubits exist in multiple states simultaneously (superposition), outperforming binary classical bits.
- Superposition & Entanglement: Superposition allows processing dense data; entanglement links qubits instantly for enhanced computing.
- Quantum Circuits: Use gates to manipulate qubits' states, allowing complex calculations.
Quantum vs. Classical Computing Differences:
- Data Processing: Qubits process exponentially more data than classical bits.
- Entanglement: Allows rapid data sharing versus classical computers’ limitations.
- Problem Solving: Quantum machines excel at complex tasks like encryption breaking and molecular predictions.
Applications & Advancements:
- Industries: Medicine (drug discovery), finance (risk management), and transport (logistics).
- Breakthroughs: Error correction advances and "quantum supremacy" achieved by Google.
Challenges:
- Technical Issues: Qubit stability and resource-intensive error correction.
- Scalability: Requires better materials, infrastructure, and trained professionals.
Future Outlook:
- AI Impact: Faster, smarter AI development.
- Predictions: Quantum supremacy expected in 20 years.
- Scalability Navigation: Industry collaboration and research progression.
Are you ready to dive into the future of gaming with quantum computing? Quantum technology could change mobile gaming as we know it! Imagine devices faster than ever, offering richer and more immersive games. In this blog, I’ll explore the core principles, major differences, and future outlook of quantum computing. Let's learn how this tech could turbocharge your gaming fun and impact the world beyond!
What Are the Core Principles of Quantum Computing?
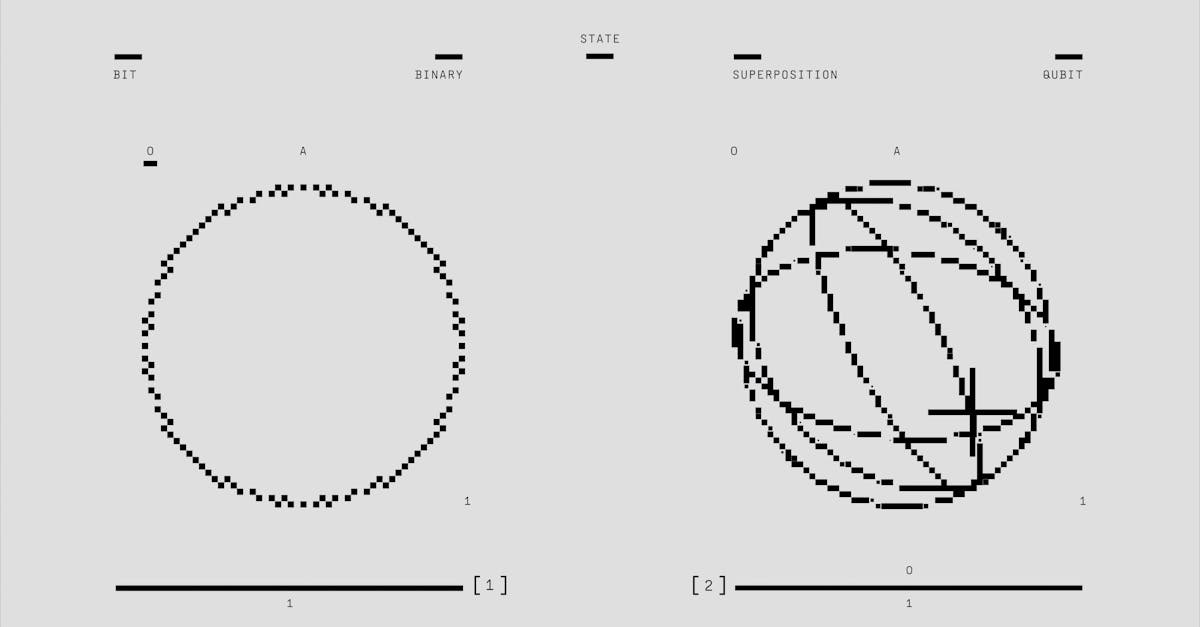
Let's dive into what makes quantum computing tick. Imagine a world where computers can solve complex problems in minutes. Sounds cool, right? This is what quantum computing aims to achieve.
How Do Quantum Bits (Qubits) Function?
Qubits are the building blocks of quantum computers. So, how do they function? The precision of the answer: Qubits can exist in multiple states at once. Unlike classical bits, which are either 0 or 1, qubits can be both. This ability to hold more information is called superposition. It makes quantum computers powerful and fast.
Superposition lets a qubit hold many possibilities. Picture a spinning coin. Instead of heads or tails, it hovers in between. Researchers work hard to harness this power because it can solve tasks that baffle today's computers.
What Is the Role of Superposition and Entanglement in Quantum Computing?
These concepts are key to quantum's magic. But what is superposition's role? The precision of the answer: Superposition allows qubits to process more data at once. This potential increases a computer's power drastically.
Now, let's talk entanglement. What's its role there? The precision of the answer: Entangled qubits can influence each other instantly, even from afar. This is a special link that boosts computing strength. Albert Einstein described it as "spooky action at a distance"! Entanglement allows quantum computers to unite qubits, enhancing their problem-solving skills.
How Do Quantum Circuits Operate?
So, how do circuits in these computers work? The precision of the answer: Quantum circuits use gates to manipulate qubits' states. Gates change qubits' superposition and entanglement for calculations.
Think of circuits like an orchestra, where gates are instruments. They control qubit states to perform complex math. This synchronization beats even powerful classical computers.
These circuits let us program quantum computers. It's like a maestro conducting a symphony, leading a new era of computing. Explore more here to grasp how they could transform our tech world.
That's why this technology is exciting. By harnessing qubits, superposition, entanglement, and circuits, quantum computing could spark the next tech revolution. Scientists believe it holds answers to problems once thought impossible.
How Does Quantum Computing Compare with Classical Computing?
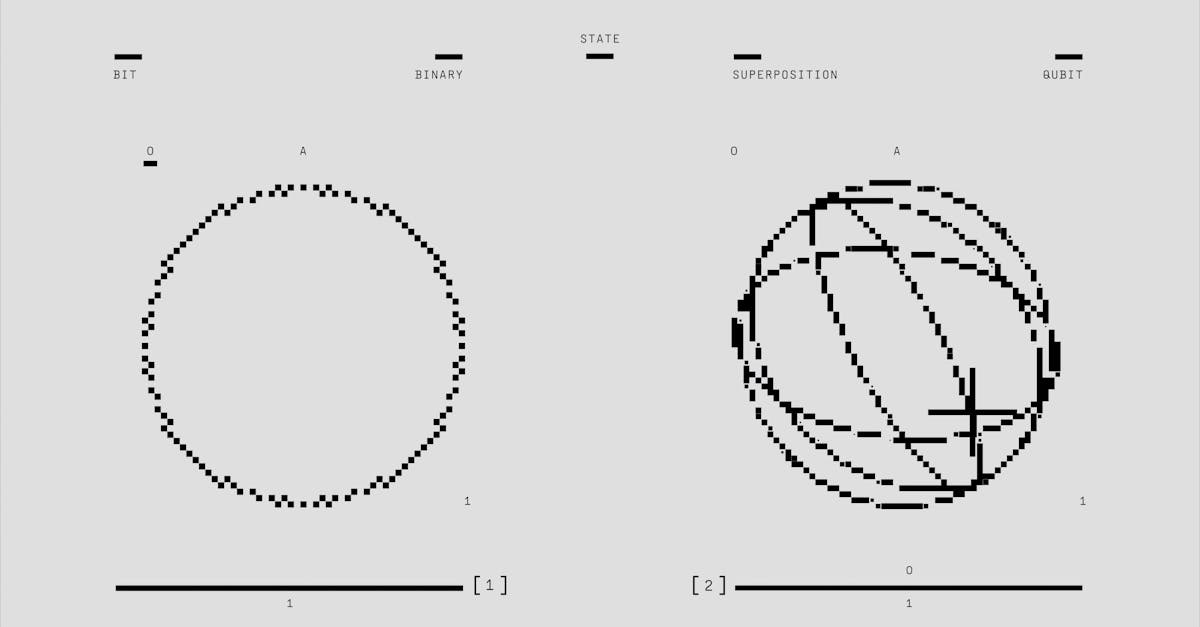
What Are the Key Differences Between Quantum and Classical Computers?
Classical computers use bits to process information. Each bit can be a 0 or a 1. This digital system is simple but powerful. Quantum computers, however, use qubits. A qubit can be a 0, a 1, or both at the same time, thanks to something called superposition. This allows quantum computers to handle more data points at once.
Another key feature in quantum computing is entanglement. Entangled qubits can connect with each other, even when far apart. This enables them to share information very quickly. Classical computers don't have this ability; they can't connect bits like qubits do.
These two differences—superposition and entanglement—allow quantum computers to solve complex problems faster. Classical computers might take years to solve some of these problems. With quantum supremacy, quantum machines can outperform the power of the best supercomputers, click here if you would like to dive deeper into quantum supremacy.
In What Scenarios Do Quantum Computers Outperform Classical Ones?
Quantum computers shine in specific scenarios. One example is encryption breaking. Classical computers struggle with certain types of encryption. Predicting molecules’ behavior also excites scientists. Classical computers can’t manage all the data needed for these predictions.
Speed is another major factor where quantum earns its stripes. The famous Shor's algorithm can factor large numbers quickly. Classical computers find this task cumbersome. Imagine trying to crack a code that guards treasure. Quantum smarts get it done in a heartbeat.
Optimization problems also favor quantum logic. Think of finding the best route to roll out new products across many cities? Quantum machines make quick work of testing each possible path.
It’s crucial to note that quantum technology still grows. Classical computers remain handy for everyday tasks. Most places you browse online use classical ones. They find the best prices and send your emails quick.
Quantum computing promises a bright future, but it’s not a universal tool. Many current tasks still rely on classical brains due to their predictable and steady nature. Therefore, until quantum tech matures, the two will likely operate side by side.
Quantum computing is thrilling due to its potential to revolutionize fields like cryptography or chemistry. Yet, classical computers still serve crucial functions that keep the digital world moving forward. Each has strengths, and their combined use might lead to the best outcomes.
What Are the Current Applications and Advancements in Quantum Computing?
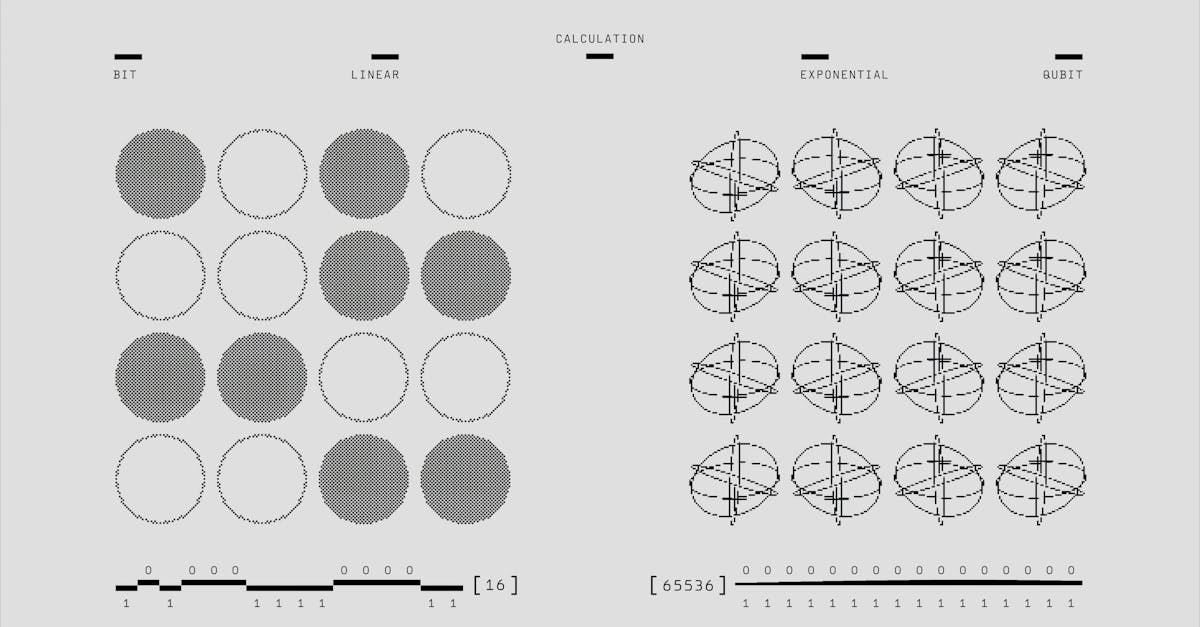
Quantum computing is changing the way we think about solving problems. It can tackle tasks that stump even the best computers today. Let's look at some fields where quantum computing is already shining.
Which Industries Are Benefiting from Quantum Computing?
Medicine is one field reaping benefits. Researchers use quantum computers to speed up drug discovery. These computers can simulate molecular interactions fast, reducing research time. Quantum computing also helps in finding new materials with unique features for manufacturing.
Finance industries are diving into quantum computing, too. They use it to optimize portfolios and manage risk better than ever. Banks get quicker results on complex calculations. It allows them to adapt fast to market changes.
Transport industries use it to solve logistics puzzles. By tackling these tough problems, they save fuel and time, making services more efficient.
What Are the Latest Breakthroughs in Quantum Technology?
A few latest breakthroughs stand out. Researchers at Google have shown how their quantum computer, Sycamore, could do calculations quicker than a classical computer. This is known as "quantum supremacy."
Another exciting development is in error correction. Quantum methods usually involve errors due to delicate systems. Recent advances now promise more stable systems with fewer errors.
Also, some experts project further leaps in quantum machine learning. This can lead to faster artificial intelligence solutions, offering faster data analysis.
How Is Quantum Computing Being Used in Cryptography?
Cryptography ensures that our data stays private. Quantum computing can change this field in two ways. First, it can break current encryption methods using its power. This raises concerns about data safety.
But quantum computing also offers solutions. It can create quantum keys that are nearly impossible to crack. This makes data exchanges over the internet safer.
Start thinking of quantum cryptography like a super strong lock. This lock uses the natural properties of particles to keep messages safe. This new cryptography method has the potential to change how we protect information in the future.
Overall, quantum computing offers exciting promises across different fields. Current advances show how versatile and influential it might become. Each breakthrough propels us closer to solving the next big global challenge. With a keen eye on these applications and advancements, we can prepare to welcome the benefits that quantum technology offers.
What Are the Challenges Facing Quantum Computing Development?

Quantum computing sounds exciting, but it faces many challenges. We need to understand what holds back its progress. Let’s explore these barriers in detail, starting with the technical difficulties.
What Are the Technical Challenges in Developing Quantum Computers?
Building quantum computers is hard. One big challenge is keeping qubits stable. Qubits store and process information but are very fragile. Even the slightest noise can mess up their state. This makes quantum computers hard to design and build. Scientists need special environments to keep qubits from errors. Small changes in temperature or electromagnetic interference can cause mistakes. Unlike classical computers, which use stable digital bits, qubits need much more precision.
Another technical problem is finding enough reliable qubits. Right now, they are costly and scarce. In classical computing, we can stack transistors easily, which brings more processing power. For quantum computers, every qubit needs careful setup and control. This complexity increases the difficulty of scaling up the machines. Unlike digital computers, which have improved with consistent technology advances, quantum tech is still improving basic components.
How Important Is Quantum Error Correction?
Quantum error correction is very important. It’s what helps us fix mistakes in quantum computers. Errors in qubits can ruin calculations. Correcting them is complex but necessary. Classical computers already use error correction for data accuracy. Quantum error correction must be even better. It needs to work in real-time, with no delays. Researchers are finding ways to fix errors without halting the computation process. This means using extra qubits to analyze and correct errors.
Quantum error correction requires a lot of resources. You need more qubits just to correct errors in your main qubits. This adds to the challenge of producing efficient quantum computers. Unlike classical error correction, which is simple and cheap, quantum error solutions are resource-heavy. This makes it hard to produce systems that are cost-effective and reliable.
What Are the Barriers to Scaling Quantum Technologies?
Scaling quantum technology is tough because many factors are in the way. First, we need better materials. Current systems rely on very rare and special materials. Finding materials that work well, last long, and are not expensive is a big task. These materials are critical for creating qubits that last longer and perform better. There's also the issue of making sure that while scaling up, the systems do not lose their unique properties.
Infrastructure presents another barrier. Quantum labs need special conditions that are difficult to maintain on a large scale. These conditions include ultra-low temperatures and precision engineering. Deploying quantum technologies calls for massive financial and technical investment. Unlike building supercomputers, which use existing knowledge, quantum computers require new approaches.
There's also a lack of skilled professionals in this field. Quantum computing is very new, so there are not enough experts. Training this workforce is crucial for scaling technologies. Unlike many digital innovations that benefit from a broad skill base, quantum tech needs new experts. Building this expertise over time is another layer of challenge for the industry.
What Is the Future Outlook for Quantum Computing?
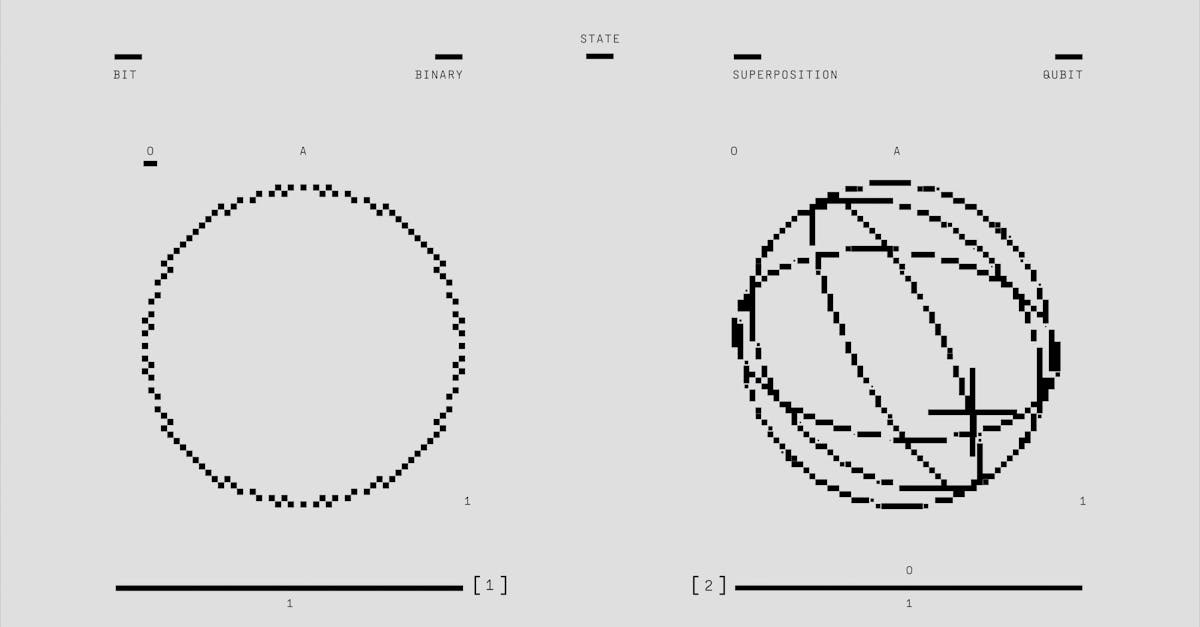
How Will Quantum Computing Impact Artificial Intelligence?
Quantum computing will boost artificial intelligence (AI) in amazing ways. With quantum computers, AI can solve problems much faster. Imagine AI getting the answer in seconds, not hours. This speed-up happens because quantum computers process data in new ways. Unlike classical computers, which use bits, quantum computers use something called qubits. Qubits can handle multiple possibilities at once. This allows AI to look at more options quickly and find better solutions. Quantum computing helps AI learn faster and more accurately which means smarter robots, improved language tools, and better healthcare diagnosis.
What Are the Predictions for Quantum Computing's Future Evolution?
Quantum computing's future seems bright and full of potential. It's expected to serve major roles in many industries, solving problems we can't tackle now. For example, pharmaceutical companies will discover new drugs faster, thanks to quantum computing's power. Also, it will help provide improved climate models, crucial for addressing environmental issues. The vision involves enhancing today's processing power to levels beyond current limitations. There's talk of reaching "quantum supremacy," where quantum computing will surpass classical computing methods. Experts believe this will happen within the next 20 years, although it remains a challenging goal.
How Can the Industry Navigate Scalability Challenges?
Scalability challenges in quantum computing are real, but the industry has a plan. Experts focus on ways to build larger quantum computers that work well. The key issue is how to increase the number of qubits and keep them stable. Qubits are very sensitive and can lose data easily. Scientists work on improving qubit technology to stop errors. They use "error correction" to help maintain stable qubits. Companies are teaming up to share ideas and learn from each other. Collaboration speeds up progress. As technology improves, we can build bigger, better quantum computers that solve harder problems. The industry's shared goal is to tackle these challenges by working together, combining resources, and continuing research.
Conclusion
We uncovered how quantum bits (qubits) use superposition and entanglement to operate. Quantum circuits work differently than classical ones, offering unique advantages. Quantum computing pushes past classical limits, excelling in specific tasks. Industries like cryptography and AI benefit from recent breakthroughs. But challenges like quantum error correction remain. The future looks promising, with continuous growth and impact on AI and other fields. Quantum computing holds transformative power, and its journey is just beginning. Keep an eye on its developments, as this technology evolves and reshapes our world.






